Have you heard of the term “Screen for life”? Well, health screening is one of the most important measures that every state and country takes for the benefit and well bring of the public. Like every other country, Singapore also brings this important health screening to life. What is Screen For Life Singapore? The screen for life importance in Singapore is initiated for public health concerns to encourage and regulate health screening. Its main motive is to detect disease earlier and treat it. If any symptoms can be identified during the test, the respective precautions will be taken to prevent the individual from future health issues. People secure all their belongings. For example, people kept their money in lockers to prevent it from stealing or theft, hired security to prevent trespassers, and installed CCTV cameras to check suspicious activities. First and foremost, preference must be given to protect our health. Screen for life is a preventive measure to identify the issues or problems in your health and treat them.
A fatal disease like cancer can be curable. At the same time, it is identified in the earlier stages if any symptoms or staging stage of cancer can be identified earlier when we regularly take tests. Taking care of your and your family’s health is a priority for leading a happy life together.
There are many screening services that are provided by health screening clinics. You may talk to your treating doctor to understand which one would you need to go ahead with. Also, a good idea is to check if a complete health screening is required or not.
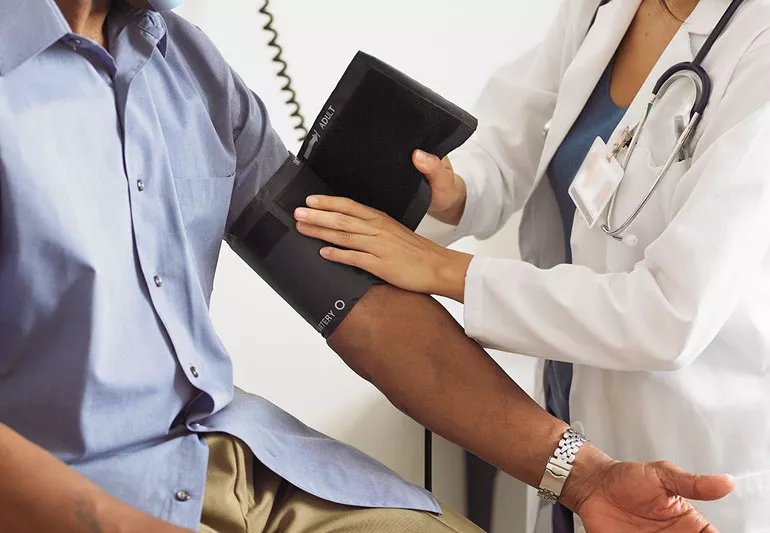
Health screening clinics play a major role in taking preventive measures for health issues by providing various services planned to diagnose health issues in the early stages before they become serious illnesses.
The services offered by health screening clinics are early detection of diseases, personal health care, and health management. It helps people to maintain their health and prevent them from illness.
Health screening clinics are places that are designed with different facilities to evaluate and diagnose diseases in an earlier stage, the current stage of existing diseases, and certain health problems before they show symptoms because these clinics offer routine evaluation. The screening test helps to identify several illnesses like cardio disease, diabetes, cancer, and other health issues like chronics. Find the best health screening clinics in Singapore to get started.